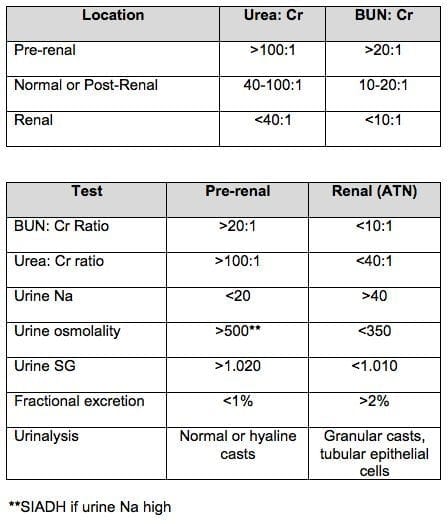
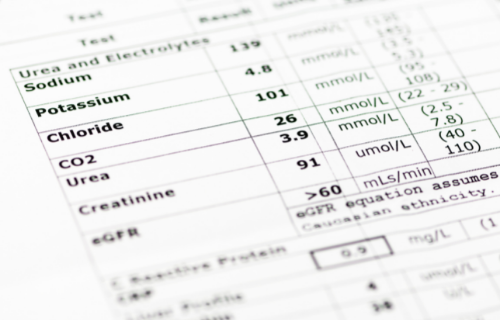
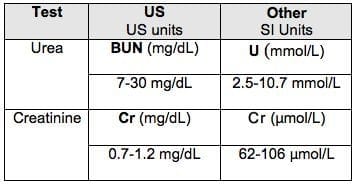
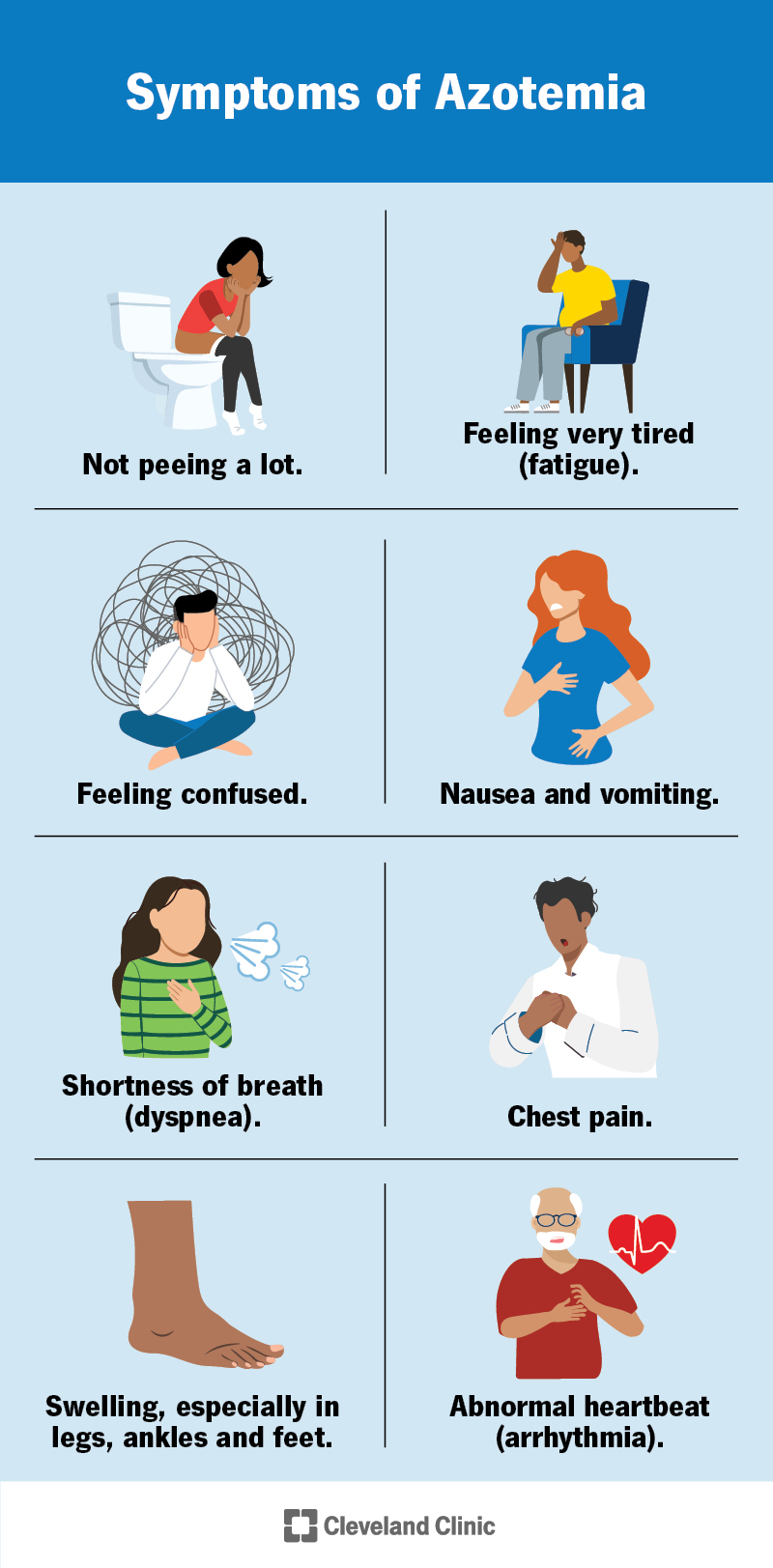
Persistent high blood urea nitrogen level is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular events in patients with acute heart failure - Jujo - 2017 - ESC Heart Failure - Wiley Online Library
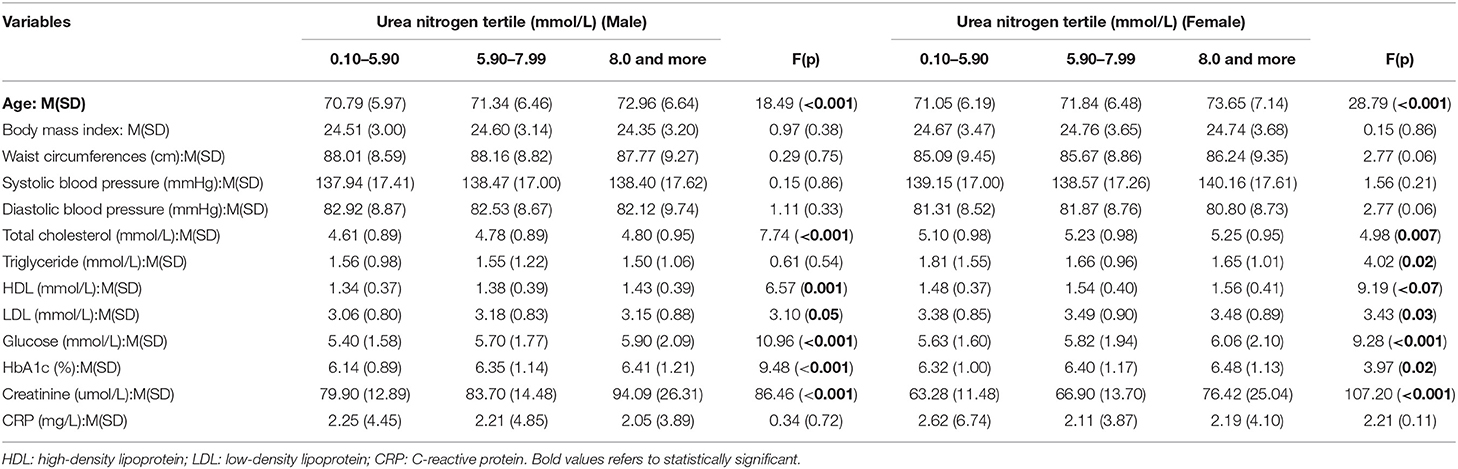
Frontiers | The Value of Blood Urea Nitrogen in the Prediction of Risks of Cardiovascular Disease in an Older Population

High urea induces depression and LTP impairment through mTOR signalling suppression caused by carbamylation - eBioMedicine
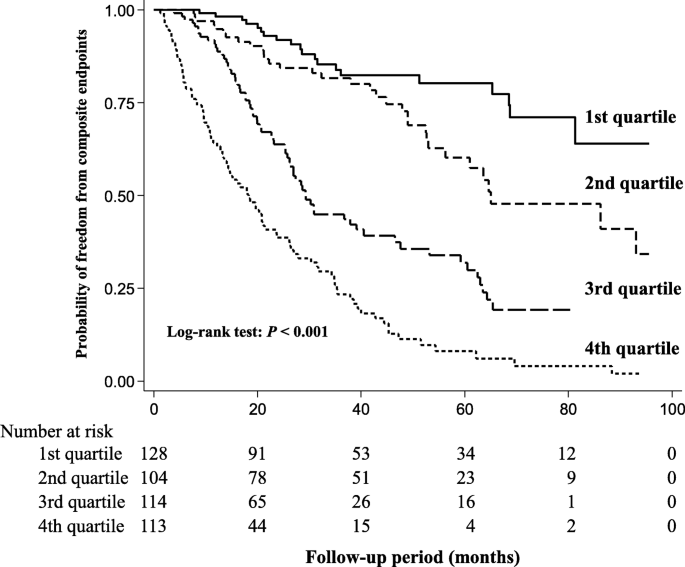
Blood urea nitrogen is independently associated with renal outcomes in Japanese patients with stage 3–5 chronic kidney disease: a prospective observational study | BMC Nephrology | Full Text
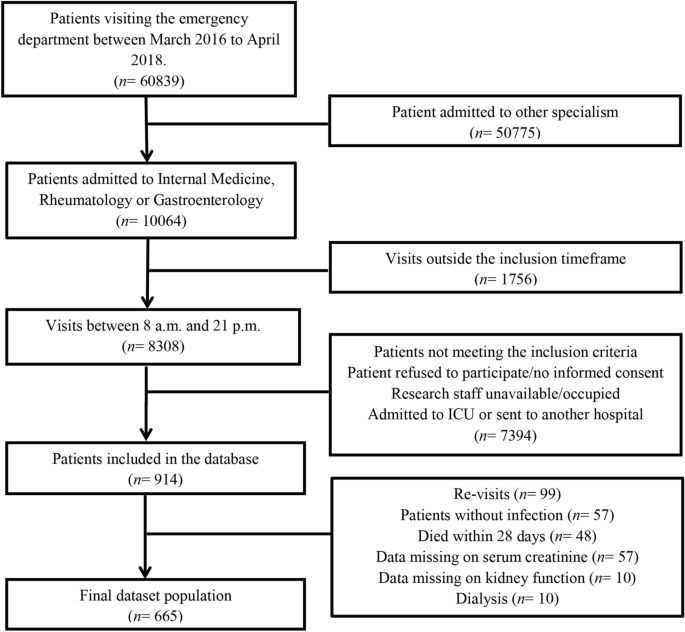
A high urea-to-creatinine ratio predicts long-term mortality independent of acute kidney injury among patients hospitalized with an infection | Scientific Reports

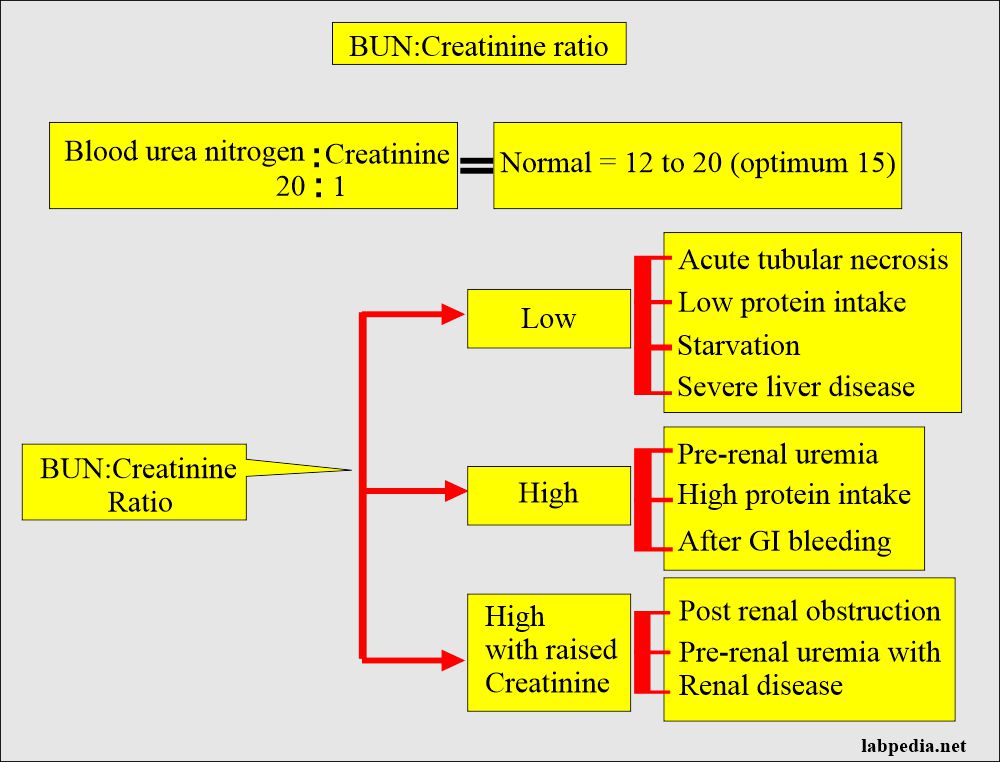

![PDF] Assessment of creatinine and urea blood levels in healthy volunteers | Semantic Scholar PDF] Assessment of creatinine and urea blood levels in healthy volunteers | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/4ac859a62619aba808ce78f34854c69db75f67eb/2-Table2-1.png)